What is Root Cause Analysis? Process, Tools, Examples
Appinio Research · 22.11.2023 · 29min read

Content
Are you tired of addressing the same problems repeatedly, only to find that they resurface, seemingly on their own? In the world of problem-solving, finding lasting solutions requires delving deeper than surface-level fixes. Enter Root Cause Analysis (RCA), a systematic approach that empowers you to uncover the hidden origins of issues and address them at their core.
In this guide, we'll demystify RCA, exploring its fundamentals, techniques, processes, and the valuable role it plays across industries. Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the concept, get ready to unlock the power of RCA and pave the way for sustainable problem-solving and continuous improvement.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic and structured approach used to identify the fundamental causes of problems or issues within a process, system, or organization. It is a methodical way of looking beyond the surface symptoms of a problem to uncover the underlying factors and events that contributed to its occurrence.
RCA involves a thorough investigation, data collection, and analysis to understand the cause-and-effect relationships within a given context. By identifying and addressing root causes, organizations can prevent the recurrence of problems and make informed decisions to improve processes and systems.
Importance of Root Cause Analysis
The importance of Root Cause Analysis extends across various industries and sectors due to its numerous benefits and implications:
- Problem Prevention: RCA helps organizations prevent problems from recurring. By addressing root causes, you not only resolve the immediate issue but also put measures in place to prevent it from happening again.
- Efficiency Enhancement: Identifying and eliminating root causes of inefficiencies or errors can improve processes and increase operational efficiency. This can result in cost savings and better resource utilization.
- Cost Reduction: Frequent problems and issues can lead to financial losses. RCA helps organizations identify and mitigate factors that contribute to these losses, ultimately saving money.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: RCA provides data-driven insights into the causes of problems. Armed with this information, organizations can make more informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and prioritize areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: RCA promotes a culture of constant improvement. Organizations that routinely conduct RCAs foster a learning environment where mistakes are viewed as opportunities for growth and refinement.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying root causes helps organizations mitigate potential risks and hazards. This is especially critical in industries where safety and compliance are paramount.
- Quality Assurance: In manufacturing and quality control, RCA plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality and meeting customer expectations. It helps identify defects and deviations from standards.
- Customer Satisfaction: Organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by addressing the root causes of customer complaints and issues.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: In regulated industries, RCA ensures that organizations comply with industry-specific regulations and standards, reducing the risk of legal issues and fines.
- Problem-Solving Capability: Developing the skill of RCA equips individuals and organizations with a valuable problem-solving tool that can be applied in various contexts and situations.
In summary, Root Cause Analysis is a valuable tool for organizations seeking to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, mitigate risks, and maintain high-quality standards. It empowers organizations to address issues proactively, make data-driven decisions, and continuously improve their processes and systems.
The Purpose of Root Cause Analysis
The primary purpose of Root Cause Analysis is to answer the fundamental question: "Why did this problem occur?" This can be broken down into several key objectives:
- Identify the Underlying Causes: RCA aims to dig deep beyond the surface symptoms of a problem to uncover the root or fundamental causes. It seeks to find out what went wrong in the system or process that led to the issue.
- Prevent Recurrence: By understanding and addressing the root causes, the main goal of RCA is to prevent the problem from happening again in the future. This is achieved by implementing corrective actions and preventive measures.
- Optimize Processes: RCA often reveals opportunities for process improvement. Organizations can use the insights gained from the analysis to optimize their processes, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: RCA provides data and evidence to support decision-making. It helps organizations make informed choices regarding resource allocation, risk management, and process changes.
- Continuous Improvement: RCA is an integral part of a culture of constant improvement. It encourages organizations to learn from their mistakes, adapt to changing circumstances, and evolve their systems and practices.
- Enhance Safety and Compliance: In industries where safety and regulatory compliance are critical, RCA ensures that organizations identify and address issues that may compromise safety or lead to non-compliance.
- Customer Satisfaction: Addressing the root causes of customer complaints and issues is vital for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Quality Assurance: In manufacturing and quality control, RCA plays a vital role in maintaining product quality and meeting quality standards.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: RCA helps organizations demonstrate due diligence and compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards.
- Skill Development: Individuals and teams involved in RCA develop problem-solving skills and become more adept at identifying and mitigating issues.
In essence, the purpose of Root Cause Analysis is to drive improvements, enhance organizational resilience, and ensure that problems are not just addressed on the surface but are systematically understood and prevented from recurring. It is a valuable tool for organizations seeking to thrive in a dynamic and competitive environment while maintaining the highest quality and safety standards.
The Fundamentals of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach to problem-solving that involves delving into the core issues causing problems. Understanding the key concepts and benefits and dispelling common misconceptions about RCA is essential before you embark on the journey of problem-solving.
Key Concepts
Root Cause
At the heart of RCA lies the concept of the root cause. It's the fundamental reason behind a problem or issue. To effectively address a problem, you must identify and rectify its root cause, not just its symptoms.
Cause-and-Effect Relationship
RCA explores the cause-and-effect relationship between various factors. It helps you connect the dots and understand how different elements contribute to a problem.
Systemic Approach
RCA takes a systemic approach by considering the broader context in which a problem occurs. It encourages you to look beyond the immediate, visible issues and explore underlying systemic weaknesses.
Preventive Action
The ultimate goal of RCA is to prevent problems from recurring. It involves implementing preventive actions based on the insights gained during the analysis.
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
Understanding the benefits of RCA can motivate you to make it an integral part of your problem-solving process:
- Problem Prevention: By addressing the root causes, RCA prevents problems from reoccurring, saving you time, resources, and frustration.
- Efficiency Improvement: Optimizing processes based on RCA findings leads to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced productivity.
- Cost Reduction: Identifying and eliminating root causes can save significant amounts of money in the long run by preventing costly recurring problems.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: RCA enables data-driven decision-making by providing a deep understanding of the issues at hand.
- Continuous Improvement: RCA fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations. It encourages learning from mistakes and evolving processes to achieve better outcomes.
Common Misconceptions
Before diving into the RCA process, it's crucial to dispel common misconceptions:
RCA is Blameful
One of the most significant misconceptions about RCA is that it's about assigning blame. In reality, RCA focuses on understanding the system and its weaknesses, not individuals.
Quick Fix
RCA is a process that takes time. It requires time, effort, and a systematic approach. Rushing through RCA can lead to ineffective results.
Only for Big Problems
RCA can be applied to both small and large problems. In fact, addressing minor issues with RCA can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems.
One Size Fits All
Different situations may require different RCA techniques. It's essential to choose the most suitable approach based on the nature of the problem and available resources.
How to Prepare for Root Cause Analysis?
Before you start the actual Root Cause Analysis, proper preparation is critical. This phase involves setting clear objectives, assembling a cross-functional team, and ensuring thorough data collection and documentation.
1. Set Objectives
Setting clear objectives is the foundation of a successful RCA. Before you can solve a problem, you need to define it and determine what you want to achieve through the analysis. Here's how to approach this:
- Define the Problem: Begin by precisely defining the problem, considering its scope, impact, and the specific issues you aim to address.
- Determine Objectives: Once the problem is defined, establish clear objectives for your RCA. What are you trying to achieve? What outcomes are you seeking?
- Scope the Analysis: Identify the boundaries of your analysis. What will be included, and what will be excluded? Setting the scope helps you focus your efforts effectively.
2. Assemble a Cross-functional Team
The composition of your RCA team can significantly impact the quality and depth of your analysis. A cross-functional team brings diverse perspectives and expertise to the table. Consider the following when forming your team:
- Diverse Expertise: Include individuals with different backgrounds, skills, and knowledge relevant to the problem. This diversity enhances the likelihood of uncovering comprehensive root causes.
- Representative Stakeholders: Ensure that your team includes representatives from different departments or areas affected by the problem. This promotes a holistic view of the issue.
- Team Dynamics: Foster open communication and collaboration within the team. Create an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their insights and concerns.
3. Data Collection and Documentation
Accurate and comprehensive data are the lifeblood of Root Cause Analysis. To ensure your analysis is based on reliable information, follow these steps:
- Identify Data Sources: Determine where you can find relevant data. This may include documents, records, interviews, surveys, and more.
- Collect Data Methodically: Collect data systematically, ensuring that you gather all necessary information without bias.
- Document Everything: Thoroughly document your data, including its source, date, and any relevant contextual information. This documentation will be crucial during the analysis phase.
- Maintain Data Integrity: Safeguard the integrity of your data. Ensure that it remains accurate and unaltered throughout the analysis process.
By paying careful attention to these fundamental aspects of Root Cause Analysis, you'll set the stage for a successful and effective problem-solving journey. Proper preparation not only streamlines the process but also increases the likelihood of finding and addressing the true root causes of the problems you encounter.
Root Cause Analysis Techniques
In Root Cause Analysis (RCA), various techniques can be employed to systematically uncover the underlying causes of problems. Each technique offers a unique perspective and approach to problem-solving. Here, we delve into the four primary RCA techniques.
The 5 Whys
The 5 Whys technique is a simple yet powerful method for peeling away the layers of a problem to get to its root cause.
- Define the Problem: Start by clearly defining the problem or issue you want to address.
- Ask "Why?": Ask yourself why the problem occurred. This may lead you to another question, to which you should again respond with "Why?" Keep repeating this process until you reach a point where the answer is no longer a symptom but a fundamental cause.
- Identify the Root Cause: Eventually, you'll arrive at the root cause of the problem, which is usually a systemic issue or process failure.
The 5 Whys technique is quick, intuitive, and can be applied in various settings, from manufacturing to healthcare. It encourages deep thinking and helps you avoid surface-level solutions.
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual tool that helps identify potential causes of a problem by categorizing them into different factors.
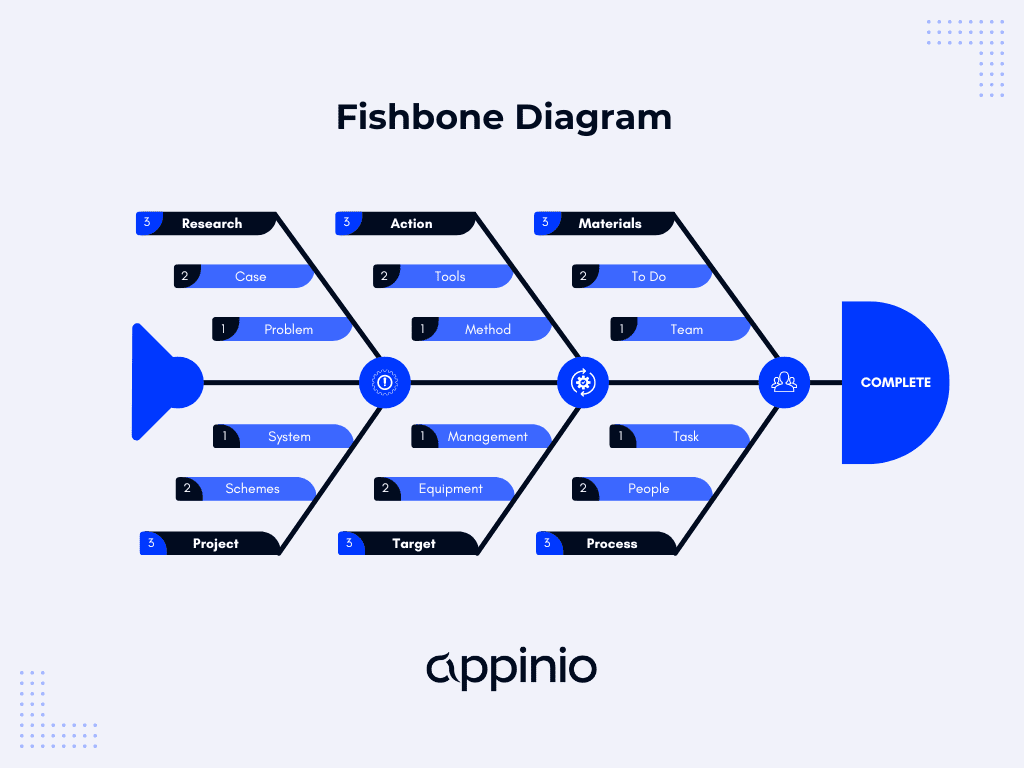
To create one:
- Define the Problem: Clearly state the problem you want to address and write it at the "head" of the fishbone diagram.
- Identify Categories: Draw the "bones" of the fishbone, representing different categories of factors that could contribute to the problem. Common categories include People, Processes, Equipment, Environment, and Materials (the 5 P's).
- Brainstorm Causes: Under each category, brainstorm potential causes or factors related to the problem.
- Analyze and Prioritize: Review the diagram to identify the most likely root causes. These are often found where multiple factors intersect.
The Fishbone Diagram is particularly useful for understanding complex problems with multiple contributing factors. It encourages group brainstorming and visual representation of the problem.
Fault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a systematic approach mainly used in engineering and safety analysis to analyze potential failures in complex systems. Here's how it works:
- Define the Top Event: Start by defining the top event, which is the undesired outcome or problem you want to understand.
- Identify Contributing Events: Identify the events or conditions that could lead to the top event. These are represented as branches and are connected logically to the top event.
- Analyze Logic Gates: Use logic gates (AND, OR) to model how different contributing events interact and lead to the top event.
- Assess Probabilities: Assign probabilities to each event and gate to calculate the probability of the top event occurring.
Fault Tree Analysis is particularly suited for industries where safety and reliability are critical, such as aerospace, nuclear power, and chemical manufacturing. It provides a systematic approach to understanding complex system failures.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying potential failure modes in a process, assessing their impact, and prioritizing them based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability.
- Define the Process: Begin by defining the process or system you want to analyze.
- Identify Failure Modes: List all possible failure modes, which are ways in which the process can fail.
- Assess Severity: For each failure mode, assess the severity of its impact on the process or end-user.
- Assess Occurrence: Estimate the likelihood of each failure mode occurring.
- Assess Detectability: Evaluate how easily each failure mode can be detected before it affects the process or customer.
- Calculate Risk Priority Number (RPN): Calculate RPN for each failure mode by multiplying severity, occurrence, and detectability scores.
- Prioritize and Take Action: Prioritize failure modes with the highest RPNs and take corrective actions to mitigate them.
FMEA is widely used in industries like automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing to proactively identify and address potential failures before they impact product quality or safety.
How to Conduct Root Cause Analysis?
The Root Cause Analysis process is a structured approach that guides you through the investigation and resolution of problems. It consists of several interconnected steps, each with its specific focus and purpose. Here's an in-depth look at the RCA process.
1. Initial Assessment
- Define the Problem: Clearly define the problem or issue that needs analysis.
- Gather Preliminary Information: Collect initial data and information related to the problem.
- Assemble a Team: Form a cross-functional team with relevant expertise to conduct the analysis.
- Set Objectives: Establish clear objectives for the RCA process, outlining what you aim to achieve.
2. Problem Identification
- Determine the Extent: Identify the scope of the problem and its impact on the organization or project.
- Document Symptoms: Record observable symptoms or issues associated with the problem.
- Create a Problem Statement: Develop a concise problem statement that articulates the issue to be addressed.
Problem Identification involves gathering information to gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem, which serves as a foundation for subsequent analysis.
3. Data Analysis
- Data Collection: Collect relevant data using appropriate methods, such as surveys, interviews, or data mining.
- Data Validation: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of collected data through verification and validation processes.
- Data Analysis Techniques: Apply statistical or analytical techniques to identify data patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Data Visualization: Use charts, graphs, and visual aids to represent data for better understanding.
Data Analysis is a crucial phase where you transform raw data into meaningful insights, helping you identify potential root causes.
4. Identify Root Causes
- Use RCA Techniques: Apply one or more RCA techniques, such as the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, Fault Tree Analysis, or FMEA, to explore potential root causes.
- Brainstorming: Encourage team members to brainstorm and generate hypotheses about the root causes.
- Prioritize Causes: Evaluate and prioritize potential root causes based on their likelihood and impact.
Identifying Root Causes is the heart of the RCA process, where you dig deep into the problem's origins to uncover what's truly responsible for the issues.
5. Verification and Validation
- Testing Hypotheses: Validate the identified root causes by testing them against the available data and evidence.
- Cross-Verification: Ensure that the identified causes align with the symptoms and issues observed.
- Peer Review: Engage in peer review to validate the findings and conclusions. Verification and Validation provide confidence that the identified root causes are accurate and truly responsible for the problem.
6. Develop Action Plans
- Create Actionable Solutions: Develop practical action plans to address the root causes, focusing on prevention.
- Assign Responsibilities: Assign responsibilities for implementing the action plans to specific team members.
- Set Timelines: Establish timelines for the implementation of corrective actions.
- Monitoring and Review: Implement a system for monitoring progress and regularly reviewing the effectiveness of the action plans.
Developing Action Plans is the final step in the RCA process, where you turn your insights into actionable strategies for preventing problem recurrence.
By following these steps in the Root Cause Analysis process, you can systematically uncover the root causes of problems, implement effective solutions, and drive continuous improvement within your organization or project.
Root Cause Analysis Tools and Software
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) can be significantly enhanced using various tools and software designed to streamline the process, improve data analysis, and visualize complex information. Here, we'll explore the key categories of tools and software used in RCA:
Data Gathering Tools
Efficient data collection is the foundation of a successful Root Cause Analysis. Utilizing the right data-gathering tools can simplify the process and ensure you collect accurate and relevant information. Some commonly used data-gathering tools include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys allow you to gather structured information from a large number of respondents. Online platforms like Appinio can help you collect data and insights in minutes.
- Interviews: Conducting interviews, whether in-person or remotely, helps you gather in-depth qualitative data. Tools like Zoom or Microsoft Teams can facilitate remote interviews.
- Observation: Observing real-time processes or events can provide valuable firsthand data. Tools like video cameras or mobile devices with recording capabilities can assist in this regard.
- Checklists: Creating checklists ensures you collect standardized data consistently. You can use simple tools like spreadsheets or specialized checklist apps.
Analysis Software
Once you've collected data, analysis software comes into play to help you make sense of the information and identify patterns and trends. Some commonly used analysis software tools include:
- Microsoft Excel: Excel is a versatile tool for data analysis, offering features for data manipulation, calculation, and visualization through charts and graphs.
- Statistical Software: Advanced statistical software like SPSS, R, or SAS is beneficial when dealing with complex datasets, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: BI tools like Tableau and Power BI are excellent for creating interactive dashboards and visualizations, enabling you to gain insights from your data more effectively.
- Root Cause Analysis Software: Specialized RCA software such as TapRooT or RCA Trainer can streamline the entire RCA process, from data collection to generating reports.
Visualization Tools
Visualizing data and information is a crucial aspect of RCA as it helps in presenting complex findings in a clear and understandable manner. Visualization tools aid in creating meaningful charts, diagrams, and reports. Commonly used visualization tools include:
- Microsoft PowerPoint: PowerPoint is a widely used tool for creating presentations that visually communicate the results of RCA. It's excellent for creating slides with charts, graphs, and diagrams.
- Lucidchart: Lucidchart is a versatile diagramming and visualization tool that allows you to create flowcharts, process maps, and other visual representations of your RCA findings.
- Tableau Public: Tableau Public is a free data visualization tool that enables you to create interactive and shareable dashboards and charts.
- Infographic Software: Tools like Canva or Piktochart are ideal for creating visually appealing infographics that summarize RCA findings for a broader audience.
Root Cause Analysis Examples
To gain a deeper understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and its practical applications, let's explore some real-world examples where RCA has played a pivotal role in problem-solving and process improvement across various industries:
Healthcare Industry
Problem: Increased surgical infection rates in a hospital's operating rooms.
RCA Process:
- Initial Assessment: The hospital management recognized the rising infection rates as a critical issue affecting patient safety and overall hospital reputation.
- Problem Identification: Surgical infection data were analyzed, and it was found that a specific operating room had consistently higher infection rates than others.
- Data Analysis: Patient records, sterilization protocols, and surgical procedures were examined to identify potential factors contributing to the problem.
- Identifying Root Causes: The RCA team discovered that inadequate sterilization procedures and inconsistent hand hygiene practices in that particular operating room were the root causes of the higher infection rates.
- Verification and Validation: Further observations and testing confirmed these findings.
- Developing Action Plans: The hospital implemented stricter sterilization protocols, provided additional training to the operating room staff on hand hygiene, and improved monitoring.
Outcome: Infection rates in the identified operating room decreased significantly, leading to improved patient safety and overall quality of care.
Software Startup
Problem: A software startup is experiencing frequent application crashes, leading to user dissatisfaction and a high churn rate.
RCA Process:
- Initial Assessment: The startup notices a surge in customer support requests and negative app store reviews, primarily due to application crashes.
- Problem Identification: Analysis reveals that the crashes occur most frequently on devices with a specific operating system version.
- Data Analysis: Crash reports, user feedback, and device-specific data are analyzed to pinpoint the root causes of the crashes.
- Identifying Root Causes: The RCA team discovers that a recent software update from the operating system provider introduced compatibility issues with certain app features, leading to crashes.
- Verification and Validation: Extensive testing and cross-referencing with device and operating system data confirm the correlation between the software update and the crashes.
- Developing Action Plans: The startup works on an app update that includes patches and workarounds to address the compatibility issues introduced by the operating system update.
Outcome: By addressing the root cause – the compatibility issues with the operating system update – the startup successfully reduces application crashes, improving user satisfaction, lower churn rates, and a more positive reputation in the market.
Manufacturing Industry
Problem: Frequent machine breakdowns in a manufacturing plant.
RCA Process:
- Initial Assessment: The manufacturing plant experienced downtime due to recurring machine breakdowns, resulting in production delays and increased maintenance costs.
- Problem Identification: The plant management observed that breakdowns primarily occurred in one specific machine.
- Data Analysis: Machine maintenance records, equipment logs, and maintenance procedures were examined to understand the causes of breakdowns.
- Identifying Root Causes: The RCA team discovered that inadequate lubrication and irregular maintenance schedules for the problematic machine were the root causes of frequent breakdowns.
- Verification and Validation: Continuous monitoring and data collection confirmed the correlation between poor maintenance practices and machine breakdowns.
- Developing Action Plans: The plant implemented a rigorous maintenance schedule, improved lubrication procedures, and provided training to maintenance personnel.
Outcome: Machine breakdowns decreased significantly, improving production efficiency and cost savings.
Retail Industry
Problem: A retail chain experiences a significant increase in customer complaints about product quality.
RCA Process:
- Initial Assessment: The retail chain notices a surge in customer complaints about the quality of certain products, affecting their reputation and sales.
- Problem Identification: A closer examination reveals that most complaints are centered around a specific product category.
- Data Analysis: Customer feedback, product testing data, and supplier records are analyzed to understand the factors contributing to the quality issues.
- Identifying Root Causes: The RCA team recognizes that a change in the supplier for the specific product category led to variations in product quality due to differences in manufacturing processes and materials used.
- Verification and Validation: Further product testing and supplier audits confirm the link between the change in supplier and the decline in product quality.
- Developing Action Plans: The retail chain decides to either revert to the previous supplier or collaborate closely with the current supplier to align quality standards and manufacturing processes.
Outcome: By addressing the root cause – the change in supplier and its impact on product quality – the retail chain successfully reduces customer complaints, maintains its reputation, and restores customer confidence, leading to increased sales.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of Root Cause Analysis across different industries. RCA not only helps identify and address the root causes of problems but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and proactive problem-solving. By systematically investigating and mitigating root causes, organizations can enhance safety, optimize processes, and achieve better outcomes for their stakeholders.
Tips for Effective Root Cause Analysis
Successful Root Cause Analysis goes beyond techniques and tools; it also involves effective practices and approaches. Here are some tips to enhance your RCA efforts.
Communication and Collaboration
- Open and Honest Communication: Encourage team members to share their observations and insights openly. Foster an environment where everyone feels comfortable expressing their ideas and concerns.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Collaborate with individuals from different departments and expertise areas. Diverse perspectives often lead to more comprehensive RCA results.
- Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed throughout the RCA process, ensuring they understand the progress and potential impact of the analysis.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop for continuous communication and adjustment of the RCA process as needed.
Avoiding Blame and Assumptions
- Focus on the System: Emphasize that RCA is about understanding the system, not assigning blame to individuals. Encourage the team to look beyond human errors and consider systemic issues.
- Challenge Assumptions: Question assumptions made during the analysis process. Avoid jumping to conclusions based on preconceived notions.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Rely on data and evidence rather than assumptions when identifying root causes. Ensure that conclusions are well-supported by the available information.
- Constructive Feedback: If errors or issues related to human actions are identified, provide feedback in a constructive and non-punitive manner, emphasizing learning and improvement.
Continuous Improvement
- Learning from RCA: View RCA as a learning opportunity. Use the insights gained from the analysis to drive continuous improvement in processes and systems.
- Implement Changes: Ensure that action plans resulting from RCA are implemented promptly. Monitor the effectiveness of these changes and make further adjustments as necessary.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of the RCA process, findings, and actions taken. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future reference and learning.
- Training and Education: Invest in training and educating team members in RCA techniques and best practices to enhance the organization's problem-solving capabilities.
Conclusion for Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is your key to solving problems effectively and preventing them from coming back. By digging deep, identifying the true causes, and taking action, you can make lasting improvements in any field, from businesses to manufacturing plants and beyond. So, remember, when faced with a problem, don't just treat the symptoms – find the root, and you'll unlock a world of solutions.
With the tips, techniques, and tools we've explored in this guide, you now have the knowledge to embark on your own RCA journey confidently. Whether you're striving for better quality, safety, or efficiency, RCA is your trusted companion in the quest for continuous improvement.
How to collect survey insights for Root Cause Analysis?
Imagine conducting your own market research in minutes, gaining real-time consumer or employee insights to validate your Root Cause Analysis (RCA). Appinio, the real-time market research platform, empowers you to collect data via surveys for RCA:
- Lightning-Fast Insights: From questions to insights in minutes, Appinio accelerates your RCA process, allowing you to pinpoint root causes swiftly.
- User-Friendly: No PhD in research needed! Appinio's intuitive platform ensures that anyone can harness the power of market research for RCA.
- Global Reach: Define your target group from 1200+ characteristics and survey it in over 90 countries, providing diverse perspectives for your analysis.
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!


