What is Gap Analysis? Steps, Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 02.11.2023 · 35min read

Content
Are you striving to bridge the divide between where your business currently stands and where you aspire it to be? Gap Analysis holds the key to unlocking your organization's full potential. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Gap Analysis, unraveling its significance, methodologies, and real-world applications.
Whether you're seeking to enhance performance, seize market opportunities, or fortify your competitive edge, this guide equips you with the tools and knowledge to navigate the path toward your desired future state.
What is Gap Analysis?
Gap Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to assess the difference, or "gap," between the current state of a business or organization and its desired state. It involves evaluating existing processes, performance, capabilities, and outcomes against predefined goals and objectives.
The goal of Gap Analysis is to identify areas where there is a discrepancy between the current state and the desired state, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and develop action plans to bridge those gaps.
Purpose and Goals of Gap Analysis
The goals of Gap Analysis can vary depending on the specific context and objectives, but they typically include:
- Identifying Gaps: The primary goal is to identify and document gaps between the current state and the desired state in various aspects of the business, such as processes, performance, or capabilities.
- Setting Objectives: Gap Analysis helps establish clear and measurable objectives and goals that are realistic and attainable.
- Developing Action Plans: It facilitates the creation of action plans to bridge the identified gaps. These plans outline the steps, resources, and timelines needed for improvement.
- Monitoring Progress: Gap Analysis supports ongoing monitoring and measurement of progress toward closing the gaps, ensuring that initiatives remain on track.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: It assists in optimizing the allocation of resources by directing investments to areas that will yield the greatest impact.
Benefits and Advantages of Conducting Gap Analysis
Conducting Gap Analysis offers numerous benefits and advantages for organizations:
- Informed Decision-Making: Gap Analysis provides data-driven insights that enable informed decision-making, helping organizations prioritize actions and investments.
- Strategic Focus: It helps businesses align their strategies with achievable goals and objectives, reducing the risk of pursuing unrealistic targets.
- Resource Efficiency: By pinpointing areas where resources can be most effectively allocated, Gap Analysis optimizes resource utilization, minimizing waste.
- Continuous Improvement: Gap Analysis fosters a culture of continuous improvement by identifying areas that require enhancement and providing a structured approach to achieving progress.
- Risk Mitigation: It helps organizations identify potential risks and vulnerabilities early, allowing for proactive risk management and mitigation.
- Competitive Advantage: Gap Analysis enables organizations to outperform competitors by addressing weaknesses and capitalizing on strengths.
- Enhanced Performance: By addressing identified gaps, organizations can improve their overall performance, customer satisfaction, and stakeholder value.
- Transparent Communication: Gap Analysis facilitates transparent communication within the organization and with external stakeholders, ensuring everyone understands the strategic direction.
- Measurable Results: It provides a basis for measuring the success and impact of improvement initiatives, ensuring that progress is quantifiable and measurable.
Overall, Gap Analysis is a valuable tool that empowers organizations to identify, address, and bridge gaps, leading to improved performance, strategic alignment, and sustainable growth.
Types of Gap Analysis
Gap Analysis can take on various forms, each tailored to address specific aspects of your business. Let's explore the four main types in detail:
Performance Gap Analysis
Performance Gap Analysis focuses on evaluating the performance of your business processes, teams, or individuals against predefined standards or benchmarks. This type of analysis helps you identify areas where your business is falling short of expectations or industry norms.
Example: Consider a manufacturing company that produces electronic devices. They set a benchmark of making 100 units per hour on their assembly line. After analyzing their actual production rate, they discover that they are only achieving 80 units per hour. This performance gap indicates inefficiencies in their assembly process.
Market Gap Analysis
Market Gap Analysis centers around understanding the gap between the demand for a product or service in the market and what your business currently offers. It helps you identify opportunities to meet unfulfilled customer needs.
Example: Imagine you run a coffee shop in a neighborhood where the majority of customers prefer specialty coffees. Your analysis reveals that you offer a limited range of specialty coffees compared to customer demand in your area. This market gap suggests an opportunity to expand your specialty coffee menu to cater to local preferences.
Competitive Gap Analysis
Competitive Gap Analysis involves comparing your business's performance, products, or services directly against those of your competitors. It helps you pinpoint where your business outperforms competitors and where it lags behind.
Example: Suppose you operate a retail clothing store, and you want to assess your competitiveness. After analyzing pricing, product quality, and customer service, you find that your prices are higher than those of your main competitors, but your product quality and customer service are superior. This competitive gap analysis suggests that you may need to reevaluate your pricing strategy while maintaining your focus on quality and service.
Product Gap Analysis
Product Gap Analysis focuses on evaluating the gap between your existing product or service offerings and what customers seek in the market. It helps you identify opportunities for product development or improvement.
Example: Let's say you own a software company that produces a project management tool.
Through product gap analysis, you discover that your competitors offer mobile app versions of their project management tools, but your product is only available as desktop software. This product gap indicates an opportunity to develop a mobile app to cater to the growing mobile-oriented market.
In summary, understanding the different types of Gap Analysis allows you to tailor your approach to the specific challenges or opportunities your business faces. Whether it's improving internal processes, addressing market demand, outperforming competitors, or enhancing your products or services, Gap Analysis provides a structured framework for decision-making and strategic planning.
How to Prepare for Gap Analysis?
Before diving into Gap Analysis, it's crucial to adequately prepare for the process. The success of your analysis depends on how well you set the stage. Here are the key steps in preparing for Gap Analysis:
1. Identify the Scope and Focus
Scope refers to the specific area of your business you intend to analyze. It could be a department, a process, or even the entire organization. Focus narrows down your analysis to particular aspects within that scope.
- Define Your Scope: Start by clearly defining the boundaries of your analysis. What aspect of your business do you want to examine? It could be marketing, sales, customer service, or any other area.
- Set Your Focus: Within your chosen scope, identify the specific elements or processes you want to analyze. For instance, if you're looking at the sales department, you might focus on lead generation, conversion rates, or customer retention.
- Align with Goals: Ensure that the scope and focus align with your overall business goals. Your analysis should directly contribute to achieving those objectives.
2. Gather Necessary Data and Information
Accurate and relevant data is the lifeblood of Gap Analysis. Gathering the right information is critical for making informed decisions.
- Data Sources: Identify the sources of data you'll need for your analysis. This may include internal sources like financial reports, customer feedback, and employee performance records, as well as external sources like market research and industry benchmarks.
- Data Quality: Ensure that the data you collect is accurate, up-to-date, and reliable. Inaccurate data can lead to misguided conclusions.
- Data Organization: Create a systematic process for collecting, organizing, and storing data. Consider using digital tools and databases to streamline this process.
- Data Accessibility: Make sure that team members who will be involved in the analysis can access the data they need easily and securely.
3. Assemble a Gap Analysis Team
Gap Analysis is not a one-person job; it requires a diverse team with various skills and perspectives. To build an effective Gap Analysis team:
- Skill Diversity: Select team members with a range of skills and expertise relevant to the scope of your analysis. For example, if you're analyzing customer service, include customer service representatives, data analysts, and process experts.
- Clear Roles: Define clear roles and responsibilities for each team member. Ensure that everyone understands their contributions to the analysis.
- Team Collaboration: Foster a collaborative environment where team members can freely share ideas, insights, and concerns. Effective communication is essential for success.
- Leadership: Appoint a team leader or project manager who can oversee the analysis process, keep the project on track, and make decisions when necessary.
4. Set Clear Objectives and Goals
Without clear objectives and goals, your Gap Analysis can quickly become aimless. Here's how to set clear goals for your analysis:
- Specificity: Make your objectives as specific as possible. Instead of a vague goal like "improve sales," aim for something like "increase monthly sales revenue by 15% within the next year."
- Measurability: Ensure that your goals are measurable. You should be able to track and quantify your progress. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) when possible.
- Relevance: Your objectives should directly relate to the scope and focus of your analysis. They should address the specific gaps you want to bridge.
- Timeframe: Set a realistic timeframe for achieving your objectives. This helps create a sense of urgency and keeps the analysis on schedule.
By effectively preparing for Gap Analysis, you lay a strong foundation for the rest of the process. Remember, the success of your analysis hinges on the clarity of your scope, the quality of your data, the synergy of your team, and the precision of your objectives. These preparatory steps ensure that your Gap Analysis is both insightful and actionable.
How to Conduct Gap Analysis?
With the preparatory work completed, it's time to delve into the core of Gap Analysis. We will guide you through the essential steps in conducting Gap Analysis effectively.
1. Data Collection and Analysis
Data is the backbone of any Gap Analysis. This phase involves gathering, organizing, and analyzing the data you've collected.
- Data Verification: Begin by verifying the accuracy and reliability of the data you've collected. Ensure that it's up-to-date and relevant to your analysis.
- Data Cleansing: Cleanse the data to remove duplicates, errors, or inconsistencies. This step is critical for ensuring your analysis is based on quality information.
- Data Organization: Organize the data in a structured manner, making it easier to work with. Consider using spreadsheets or data visualization tools to assist in this process.
- Data Analysis Tools: Utilize data analysis tools and techniques to extract insights from the data. This may involve statistical analysis, trend identification, or data visualization.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data. These patterns can provide valuable insights into the current state of your business.
You can streamline your data collection and analysis processes with the assistance of advanced technology. Appinio, a cutting-edge research platform, offers robust tools for data gathering and analysis, helping you collect insights efficiently. With our platform, you can verify data accuracy, cleanse information, and organize it seamlessly. Additionally, Appinio's data analysis capabilities enable you to identify crucial patterns and trends that inform your Gap Analysis.
Take your data-driven decision-making to the next level. Book a demo now to explore how Appinio can elevate your Gap Analysis efforts and empower your business to bridge those critical gaps effectively!
2. Identify Current State
Before you can bridge the gap, you must have a clear understanding of where you currently stand. This step involves assessing and documenting your business's current state.
- Process Mapping: Create process maps or flowcharts to visualize how critical processes operate within your business. This helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Performance Metrics: Evaluate relevant performance metrics in your chosen scope. For instance, if you're analyzing customer service, assess metrics like response times, resolution rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
- Stakeholder Interviews: Conduct interviews or surveys with key stakeholders to gather qualitative insights into the current state. Employees, customers, and suppliers can provide valuable perspectives.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: Identify the strengths and weaknesses within the scope of your analysis. Understanding these aspects is crucial for setting improvement goals.
3. Determine Desired State
Having a clear vision of where you want to be is essential for Gap Analysis. Define your desired state:
- Goal Setting: Clearly define the goals and objectives you aim to achieve through the Gap Analysis process. Ensure that these goals align with your overall business strategy.
- Benchmarking: If applicable, benchmark your desired state against industry standards or competitors' performance. This provides a reference point for your goals.
- Customer Expectations: Consider the expectations of your customers and stakeholders. What do they expect from your business, and how can you meet or exceed those expectations?
- Long-Term Vision: Think beyond immediate improvements. Consider your long-term vision for the business. What should it look like in the next three, five, or ten years?
4. Analyze the Gap
This is the heart of Gap Analysis, where you identify and quantify the gaps between your current and desired state.
- Quantification: Use metrics, KPIs, or scoring systems to quantify the gaps. This makes it easier to prioritize areas that need improvement.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate the root causes of the identified gaps. What factors or issues are contributing to the discrepancies between the current and desired states?
- Impact Assessment: Assess the potential impact of each gap on your business. Determine which gaps have the most significant consequences and should be addressed first.
- Risk Analysis: Consider the risks associated with each gap. What are the potential risks if you don't bridge these gaps? Understanding the risks can inform your decision-making.
By diligently following these steps in conducting Gap Analysis, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of your current business state, a clear vision of where you want to go, and a quantified view of the gaps that need your attention. This analysis provides the foundation for making informed decisions and developing effective action plans to bridge those gaps.
Gap Analysis Tools and Techniques
To conduct effective Gap Analysis, you can leverage a range of tools and techniques. These methods provide structured approaches to gather insights, identify gaps, and make informed decisions. Let's explore these tools and techniques in detail.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a widely used tool for assessing the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats associated with your business or a specific aspect of it. It helps you gain a holistic view of your current state and potential future directions.
- Strengths: These are the internal attributes and resources that give your business an advantage. They are what you do well and can capitalize on.
- Weaknesses: Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder your business's performance. Identifying weaknesses allows you to address areas in need of improvement.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are external factors or trends that your business can leverage to its advantage. Recognizing opportunities helps you prioritize strategic initiatives.
- Threats: Threats are external factors that can negatively impact your business. Being aware of threats allows you to develop mitigation strategies.
SWOT Analysis is a versatile tool that can be applied to various aspects of your business, from marketing and sales to operations and product development.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance, processes, or practices against those of industry leaders or competitors. It allows you to identify performance gaps and best practices that can be adopted to improve your own operations.
- Internal Benchmarking: This involves comparing different departments or teams within your organization to identify areas where one can learn from the other.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Here, you analyze how your business stacks up against direct competitors in terms of key performance metrics.
- Functional Benchmarking: Functional benchmarking compares specific business functions, such as customer service or supply chain management, with those of other organizations, even outside your industry.
Benchmarking provides valuable insights into where your business stands relative to others and highlights opportunities for improvement.
Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is a technique used to identify the underlying causes of problems or gaps within your business. It goes beyond surface-level symptoms to uncover the fundamental reasons for issues.
- Cause-and-Effect Analysis: Also known as the Fishbone Diagram or Ishikawa Diagram, this technique helps you visualize the various factors that contribute to a problem or gap. It's particularly useful for exploring complex issues.
- 5 Whys Technique: This method involves asking "why" multiple times (usually five) to drill down to the root cause of a problem. It's a simple yet effective way to dig deeper into issues.
- Fault Tree Analysis: This technique is more structured and is used for complex problems, especially in high-risk industries like aerospace and nuclear power. It traces events back to their root causes.
Root Cause Analysis is essential for addressing issues at their source rather than just treating symptoms, leading to more effective and sustainable solutions.
Fishbone Diagrams
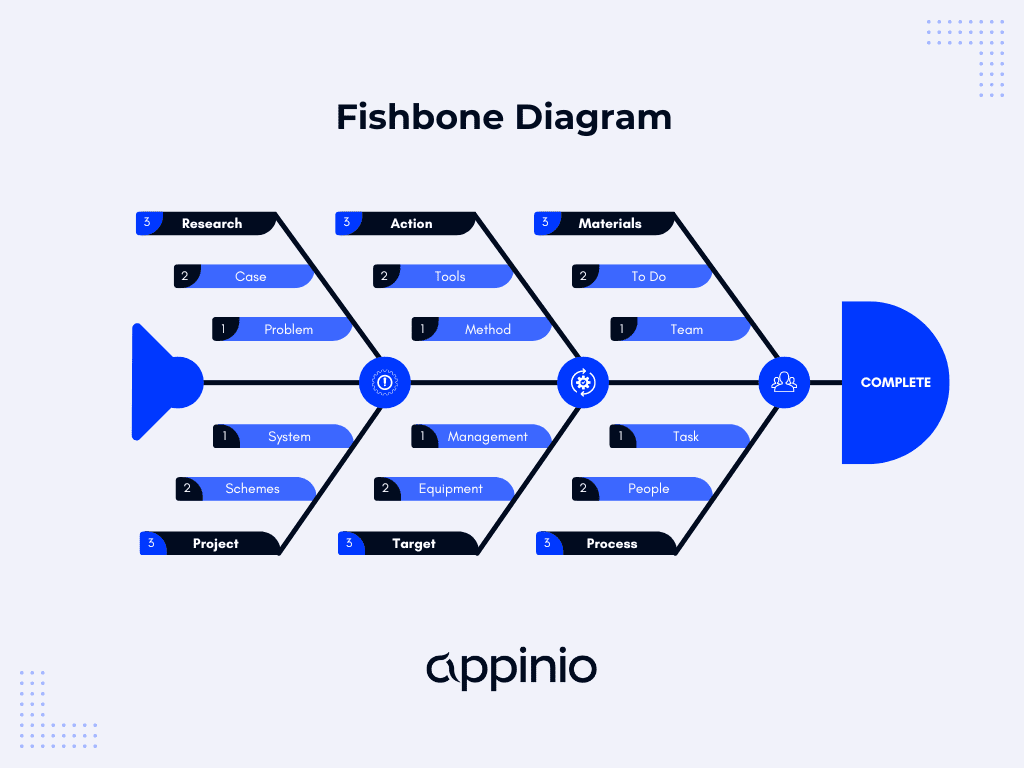
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual tool used to identify potential causes of a problem or gap. It helps you explore various factors that could contribute to an issue and discover their interrelationships.
- Categories of Causes: The diagram typically includes categories like People, Process, Equipment, Materials, Environment, and Management (the 6 M's). These categories serve as branches on the fishbone diagram.
- Identifying Causes: Under each category, you list potential causes or factors contributing to the problem. This brainstorming process encourages a comprehensive examination of the issue.
- Visual Representation: The diagram resembles a fish's skeleton, with the main problem at the "head" and the potential causes branching off like "bones."
These Gap Analysis tools and techniques provide structured approaches to gather data, analyze information, and make strategic decisions. Depending on the nature of your analysis and the complexity of the issues you're addressing, you can choose the most appropriate tool or combination of tools to support your Gap Analysis process.
Gap Analysis Template
A Gap Analysis template is a structured framework that provides a systematic approach to conducting Gap Analysis within your business. It serves as a roadmap, ensuring you cover all the necessary steps and elements during the analysis process.
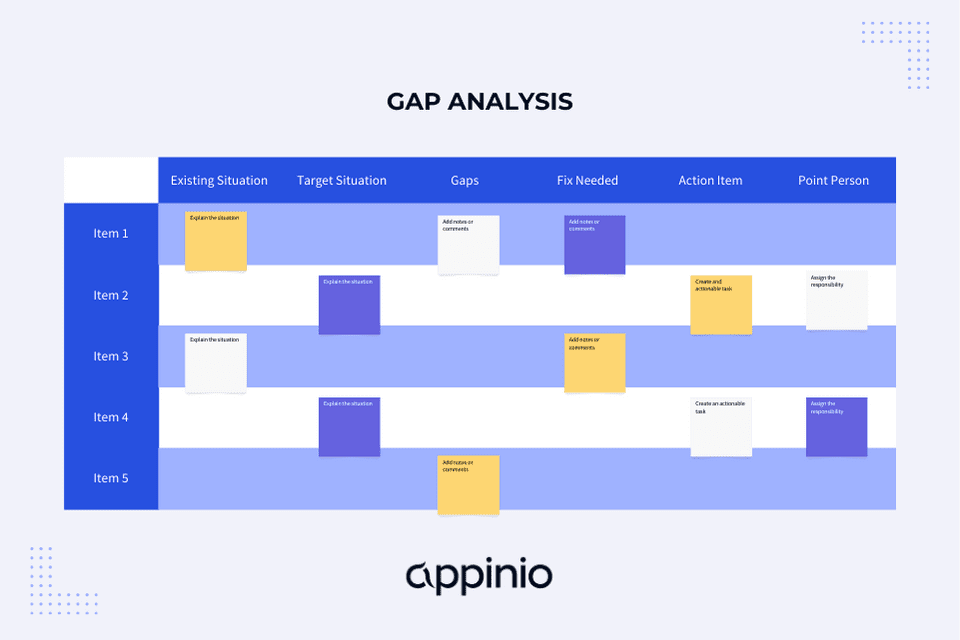
Here, we'll provide you with a Gap Analysis template and tips on utilizing it effectively.
Components of a Gap Analysis Template
A well-designed Gap Analysis template typically includes the following components:
Scope and Focus
- Clearly define the scope of the analysis. What aspect of your business will you examine?
- Specify the focus within the chosen scope. Which specific elements or processes will you analyze?
Data Collection and Analysis
- Outline the sources of data and information required for the analysis.
- Provide guidance on how to gather, verify, and organize the data.
- Include sections for data analysis techniques and tools to be used.
Identifying Current State
- Define the methods for assessing the current state within the chosen scope.
- List key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to evaluate.
- Offer guidance on documenting strengths and weaknesses.
Determining Desired State
- Specify the criteria for setting clear objectives and goals.
- Explain how to align goals with the scope and focus of the analysis.
- Encourage the inclusion of long-term visions for the desired state.
Analyzing the Gap
- Provide guidance on quantifying gaps and discrepancies.
- Offer tools and techniques for identifying the root causes of gaps.
- Include sections for assessing the impact and potential risks associated with each gap.
Recommendations and Action Plan
- Outline the format for presenting recommendations to bridge the gaps.
- Encourage the development of a comprehensive action plan.
- Include sections for resource allocation, timelines, and responsibilities.
Monitoring and Adjustments
- Describe the process for tracking progress and measuring success.
- Explain how to make necessary adjustments to the action plan.
- Emphasize the importance of continuous assessment and feedback loops.
Benefits of Using a Gap Analysis Template
Utilizing a Gap Analysis template offers several benefits:
- Structured Approach: Ensures a systematic and organized analysis process from start to finish. and provides a clear framework that guides users through each step.
- Consistency: Promotes consistency in conducting Gap Analysis across different areas or departments within the organization and helps maintain a standardized approach to data collection and evaluation.
- Efficiency: Saves time by eliminating the need to create analysis guidelines from scratch and streamlines the documentation process, making it easier to communicate findings and recommendations.
- Clarity: Helps clarify the objectives and goals of the analysis and ensures that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the analysis process and its outcomes.
- Customization: Allows flexibility for tailoring the template to the specific needs and nuances of your business and enables the inclusion of industry-specific metrics and benchmarks.
Tips for Creating an Effective Gap Analysis Template
When creating a Gap Analysis template, consider the following tips:
- Collaborate: Involve team members and stakeholders in the template's development to ensure it aligns with your business's unique requirements.
- Simplicity: Keep the template straightforward and user-friendly. Avoid unnecessary complexity that might hinder its usability.
- Flexibility: Make the template adaptable to different types of Gap Analysis, whether it's performance, market, competitive, or product analysis.
- Documentation: Include sections for documenting assumptions, data sources, and references to maintain transparency and credibility.
- Training: Provide training and guidance on how to use the template effectively to ensure consistency in analysis processes.
- Version Control: Implement version control to track updates and revisions to the template over time.
By creating and utilizing a well-designed Gap Analysis template, you empower your organization to conduct thorough and consistent analyses, enabling informed decision-making and continuous improvement across various facets of your business.
How to Interpret and Report Gap Analysis Results?
After conducting a Gap Analysis, it's essential to interpret the results effectively and communicate them to relevant stakeholders. This section will guide you through the steps in analyzing and reporting Gap Analysis findings:
1. Present Gap Analysis Results
Showcasing your Gap Analysis results in a clear and compelling manner is crucial for decision-making. Consider the following when presenting your findings:
- Visual Aids: Utilize charts, graphs, and visuals to make complex data more accessible and understandable. Visual representations can help stakeholders grasp critical insights at a glance.
- Narrative Explanation: Accompany visuals with a narrative that explains the significance of the findings. Describe the current state, desired state, and the gaps identified.
- Key Highlights: Highlight the most critical gaps or issues that need immediate attention. Focus on those that have the most significant impact on your business goals.
- Benchmark Comparisons: If applicable, compare your findings to benchmarks or industry standards to provide context and emphasize the gaps.
2. Identify Priorities and Action Items
Not all gaps are created equal. Some may have a more substantial impact on your business than others. Here's how to identify priorities and action items:
- Impact Assessment: Assess the potential impact of each gap on your business's performance, goals, and objectives. Prioritize those with the most significant consequences.
- Urgency: Consider which gaps require immediate attention due to their urgency or potential to escalate if left unaddressed.
- Feasibility: Evaluate the feasibility of closing each gap. Some gaps may be more straightforward to address, while others may require significant resources or time.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the costs of closing each gap against the expected benefits. Focus on those gaps where the benefits outweigh the costs.
3. Create an Action Plan
Once you've identified priorities, it's time to develop a comprehensive action plan to bridge the gaps.
- Specific Goals: Clearly define the goals and objectives associated with each gap. Make sure they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Tasks and Responsibilities: Break down the action plan into specific tasks and assign responsibilities to team members. Everyone should know their role in closing the gaps.
- Timelines: Establish realistic timelines for completing each task or milestone. Ensure that there are clear deadlines to keep the action plan on track.
- Resources: Identify the resources, including budget, personnel, and technology, required to implement the action plan successfully.
4. Communicate Findings to Stakeholders
Effective communication with stakeholders is essential to ensure alignment and support for your action plan:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Identify all relevant stakeholders, including executives, employees, investors, and customers, and engage them in the process.
- Transparency: Be transparent about the findings, priorities, and action plan. Provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of the rationale behind your decisions.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms that allow stakeholders to provide input and ask questions. Address concerns and adapt the action plan if needed.
- Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed of progress. Regularly update them on milestones achieved and any changes in the action plan.
- Celebrate Success: When you successfully bridge a gap, celebrate the achievement with your team and stakeholders. Recognizing success boosts morale and motivation.
Effectively interpreting Gap Analysis results and reporting them to stakeholders ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the identified gaps and the plan to address them. This transparency and collaboration are essential for achieving the desired outcomes and fostering a culture of continuous improvement within your organization.
How to Implement Gap Analysis Recommendations?
Implementing the recommendations generated from Gap Analysis is the critical phase that turns insights into action and results. Here, we'll explore in-depth the steps involved in effectively implementing Gap Analysis recommendations:
1. Allocate Resources
To bridge the identified gaps successfully, you must allocate the necessary resources, including budget, personnel, and technology.
- Resource Identification: Based on the action plan developed during Gap Analysis, identify the specific resources required for each task or initiative. This may include financial resources, additional personnel, or access to particular technology or tools.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources efficiently to ensure each task has what it needs to succeed. Prioritize resources based on the urgency and impact of each gap.
- Budget Planning: Develop a budget that outlines the costs associated with closing the gaps. Consider both direct and indirect costs, and ensure that your financial plan aligns with your business's financial capabilities.
- Personnel Deployment: Assign responsibilities to team members or departments, making sure that individuals with the necessary skills and expertise are leading each initiative.
- Technology and Tools: If your action plan involves adopting new technology or tools, ensure that you have the proper systems in place and provide adequate training to your staff.
Effective resource allocation ensures that you have the means to execute your action plan efficiently and achieve the desired outcomes.
2. Monitor Progress
Once you've allocated resources and initiated the action plan, it's crucial to continuously monitor progress to stay on track.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define and track KPIs specific to each initiative. KPIs should be measurable and aligned with the goals set during Gap Analysis.
- Regular Reporting: Establish a reporting cadence to track progress and share updates with stakeholders. This can be weekly, monthly, or as needed, based on the complexity of the initiatives.
- Performance Metrics: Continuously assess the performance of your action plan against the predetermined goals and objectives. Are you achieving the desired results?
- Issue Identification: Be vigilant in identifying any roadblocks, obstacles, or issues that may impede progress. Address these challenges promptly to keep the plan on course.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage feedback from team members involved in implementing the recommendations. Their insights can help fine-tune the approach and overcome hurdles.
Monitoring progress ensures that you're moving in the right direction and allows you to make timely adjustments when needed.
3. Make Necessary Adjustments
Flexibility is vital when implementing Gap Analysis recommendations. Be prepared to make adjustments along the way.
- Continuous Assessment: Regularly review the effectiveness of your action plan. Assess whether it's achieving the desired outcomes and closing the identified gaps.
- Feedback Integration: Act on feedback from stakeholders and team members. If they provide insights or suggestions for improvement, incorporate them into the plan as appropriate.
- Adaptation: Be open to adapting your approach if circumstances change. External factors, market dynamics, or unexpected events may necessitate adjustments.
- Resource Reallocation: If certain initiatives are not progressing as expected, consider reallocating resources to more promising areas or revising the action plan.
Making necessary adjustments ensures you remain agile and responsive, increasing the likelihood of successfully closing the gaps.
4. Measure Success and Impact
Ultimately, the success of your Gap Analysis recommendations should be measured by their impact on your business.
- Goal Achievement: Evaluate whether you've met the specific goals and objectives outlined in your action plan. Assess the degree to which the gaps have been closed.
- Performance Improvement: Measure the improvements in key performance metrics that were targeted during the Gap Analysis process. Compare current performance to the baseline.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Solicit feedback from stakeholders to gauge their satisfaction and perception of the changes made as a result of the recommendations.
- Long-Term Impact: Assess the sustainability of the improvements over time. Are the changes enduring, or do they require ongoing efforts to maintain?
By measuring success and impact, you not only validate the effectiveness of your Gap Analysis recommendations but also gain valuable insights into the long-term benefits and areas where further adjustments may be necessary.
Gap Analysis Examples
To gain a deeper understanding of how Gap Analysis is applied in various business scenarios, let's explore a range of real-world examples. These examples will illustrate how Gap Analysis can be a versatile tool for identifying and addressing gaps in different aspects of your organization.
Performance Gap Analysis
Scenario: A retail company wants to improve its inventory management processes to reduce carrying costs and stockouts.
Gap Analysis:
- Current State: The company conducts an analysis of its existing inventory management practices and identifies inefficiencies, such as overstocked items and frequent stockouts.
- Desired State: They set a goal to maintain optimal inventory levels by implementing just-in-time inventory management.
- Gap: The gap analysis reveals a significant discrepancy between the current state and the desired state in terms of inventory management efficiency.
Recommendations: The company's action plan includes investing in inventory management software, providing employee training, and optimizing supplier relationships to bridge the gap.
Market Gap Analysis
Scenario: An e-commerce startup is looking to expand its product offerings and wants to identify untapped market segments.
Gap Analysis:
- Current State: The startup analyzes its existing customer base and product offerings, noting gaps in its product range.
- Desired State: They aim to target specific demographics and offer products tailored to those segments.
- Gap: The analysis reveals that there is a significant gap between their current product offerings and the preferences of their target market segments.
Recommendations: The action plan includes market research to understand customer preferences, product development to fill the gaps, and marketing strategies to reach the new target segments.
Competitive with Gap Analysis
Scenario: A software company wants to enhance its competitiveness in the market.
Gap Analysis:
- Current State: The company assesses its product features, pricing, and customer support in comparison to key competitors.
- Desired State: They aim to offer a more feature-rich product at a competitive price point with superior customer support.
- Gap: The analysis reveals that their product features and customer support fall short compared to their competitors.
Recommendations: The action plan includes product development to add missing features, pricing adjustments, and investing in customer service training and resources.
Product Gap Analysis
Scenario: An automobile manufacturer wants to introduce a new electric vehicle (EV) to the market.
Gap Analysis:
- Current State: The company evaluates its existing product lineup and identifies the gap in EV offerings.
- Desired State: They set a goal to develop and launch an electric vehicle to meet the growing market demand for eco-friendly options.
- Gap: The analysis shows a gap between the current product lineup, which lacks an EV, and market demand for such vehicles.
Recommendations: The action plan includes research and development for the EV, securing the necessary supply chain for batteries, and marketing strategies to promote the new product.
These Gap Analysis examples demonstrate how businesses can apply this versatile tool to various scenarios, including performance improvement, market expansion, competitive positioning, and product development. By conducting Gap Analysis in these contexts, organizations can make informed decisions, set clear objectives, and develop action plans to bridge the identified gaps and achieve their strategic goals.
Conclusion for Gap Analysis
Gap Analysis is a powerful compass that guides your business from where it is to where it wants to be. By identifying gaps, setting clear goals, and taking action, you can steer your organization toward success. Remember, the journey of improvement is ongoing, and Gap Analysis is your trusty navigator on this path.
So, use these insights, tools, and techniques to continually assess, adapt, and thrive. As you bridge the gaps and achieve your objectives, you'll not only enhance performance but also foster a culture of progress and innovation within your organization. With Gap Analysis as your strategic ally, the possibilities for growth are limitless.
How to Conduct Gap Analysis in Minutes?
Discover the future of Gap Analysis with Appinio, the real-time market research platform. With Appinio, Gap Analysis becomes not just efficient but also exciting, intuitive, and accessible. Say goodbye to the stigma of boring and overpriced market research and hello to the future of informed decision-making.
-
Rapid Results: From questions to insights in minutes, Appinio's lightning-fast platform ensures you get the answers you need, precisely when you need them.
-
User-Friendly: No need for a PhD in research – our intuitive platform is designed for everyone. Seamlessly integrate market research into your everyday decision-making.
-
Global Reach: Define your target group from over 1,200 characteristics and survey respondents in 90+ countries. Appinio empowers you to make data-driven decisions on a global scale.
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!


