What is a PESTEL Analysis? Definition, Factors, Examples
Appinio Research · 03.01.2024 · 35min read

Content
Are you ready to decode the intricate puzzle of business dynamics and gain a competitive edge? In this guide, we unravel the power of PESTEL analysis – a strategic tool that delves deep into the external factors shaping industries and organizations.
Explore how this multifaceted framework enables you to anticipate change, seize opportunities, and fortify your business strategy. From deciphering political landscapes to harnessing technological revolutions, embark on a journey of strategic enlightenment as we demystify PESTEL analysis and equip you with the tools to navigate the ever-evolving business terrain.
What is a PESTEL Analysis?
PESTEL analysis is a strategic framework that helps organizations evaluate and understand the external factors that impact their operations and decision-making. The acronym PESTEL stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. These represent the various aspects of the external environment that can affect an organization's performance and long-term success.
The primary purpose of conducting a PESTEL analysis is to gain insights into the external factors that can shape an organization's strategic direction. This analysis allows businesses to:
- Anticipate Change: By examining external factors, organizations can proactively identify potential changes and trends in their operating environment, helping them stay ahead of the curve.
- Identify Opportunities: PESTEL analysis uncovers opportunities that businesses can leverage to their advantage, such as emerging markets, technological advancements, or shifting consumer preferences.
- Manage Risks: It helps organizations recognize potential threats and risks, such as regulatory changes, economic downturns, or environmental issues, allowing for risk mitigation strategies.
- Strategic Planning: PESTEL analysis informs the development of strategic plans, enabling organizations to align their goals with the external environment and create robust strategies.
- Informed Decision-Making: It provides a foundation for data-driven decision-making, ensuring that choices are grounded in a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape.
Importance of PESTEL Analysis in Business
PESTEL analysis holds immense importance in the world of business for several compelling reasons:
- Strategic Adaptation: In an ever-changing business landscape, PESTEL analysis helps organizations adapt to evolving conditions, making them more resilient and competitive.
- Market Expansion: It assists in evaluating the feasibility of entering new markets or expanding existing operations by considering the external factors at play.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential risks early, organizations can develop strategies to minimize their impact, safeguarding their profitability and reputation.
- Innovation and Opportunity: PESTEL analysis reveals opportunities for innovation, enabling businesses to develop products and services that align with emerging trends and consumer demands.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding legal and regulatory factors is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding costly legal issues.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: It provides decision-makers with a comprehensive view of the external environment, facilitating more informed and strategic choices.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that effectively utilize PESTEL analysis gain a competitive advantage by staying ahead of industry shifts and customer preferences.
In summary, PESTEL analysis is a vital tool for organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of the external business environment. It guides strategic decision-making, promotes agility, and positions businesses for long-term success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
SWOT vs. PESTEL: A Comparative Analysis
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis and PESTEL analysis are both powerful strategic planning tools used by businesses to assess their internal and external environments. Each approach offers a unique perspective on the factors that can impact an organization's success.
Understanding SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis focuses on the internal factors (Strengths and Weaknesses) and external factors (Opportunities and Threats) that can influence a business. Here's a brief overview of each component:
- Strengths: These are internal attributes or resources that give your organization a competitive advantage. They can include a strong brand, skilled workforce, or unique technology.
- Weaknesses: Internal weaknesses are areas where your organization may lag behind competitors. Identifying weaknesses allows you to address and improve them.
- Opportunities: External opportunities are favorable conditions or trends in the market that your organization can capitalize on. These can include emerging markets or new consumer trends.
- Threats: External threats are factors outside your organization that can pose risks. These may include economic downturns, competitive pressures, or regulatory changes.
SWOT Analysis vs. PESTEL Analysis
While both SWOT and PESTEL analyses are valuable tools for strategic planning, they serve different purposes and provide distinct insights.
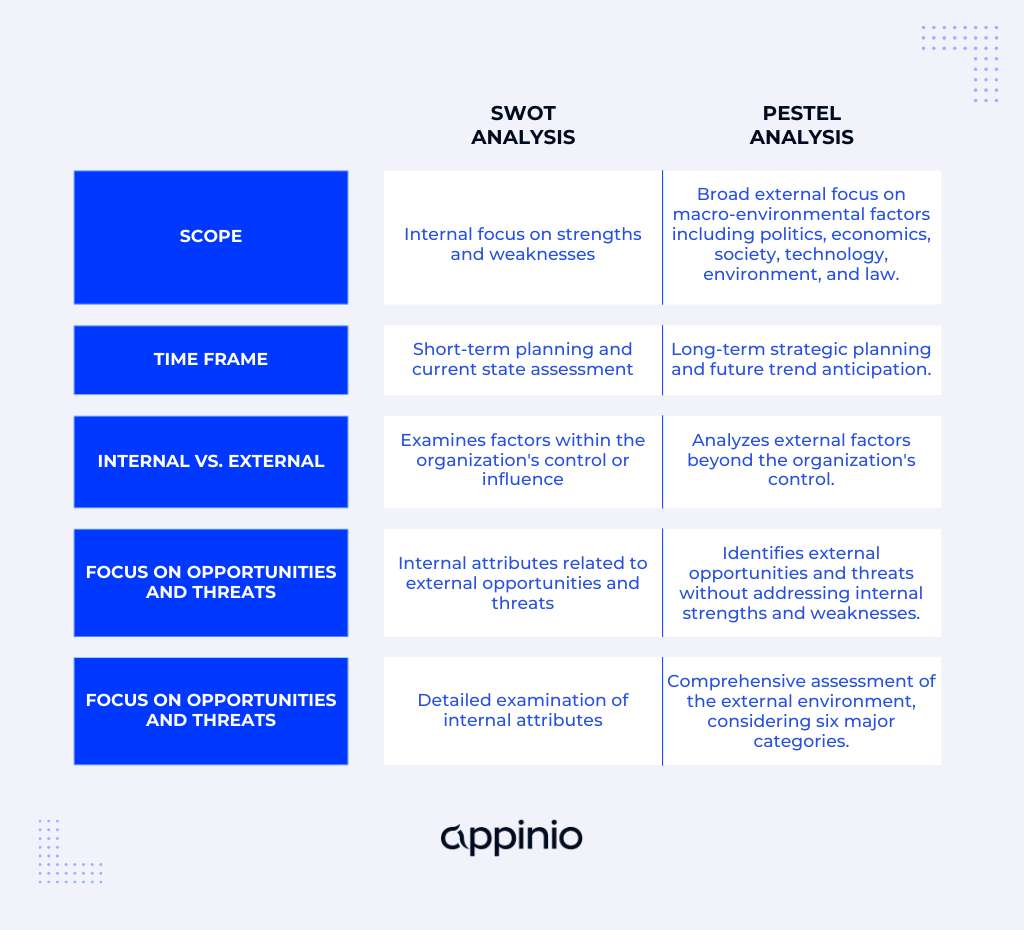
Scope
- SWOT: Primarily focuses on the internal aspects of a business, examining strengths and weaknesses. It provides a snapshot of the current state.
- PESTEL: Concentrates on the external macro-environment, exploring political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors that can impact an organization. It offers a broader perspective.
Time Frame
- SWOT: Typically used for short-term planning and immediate decision-making. It assesses the current situation.
- PESTEL: Suited for long-term strategic planning and horizon scanning. It anticipates future changes and trends.
Internal vs. External
- SWOT: Primarily examines factors within the organization's control or influence.
- PESTEL: Analyzes factors that are largely external to the organization, beyond direct control.
Focus on Opportunities and Threats
- SWOT: Explores internal strengths and weaknesses in relation to external opportunities and threats.
- PESTEL: Identifies external opportunities and threats without addressing internal strengths and weaknesses.
Depth of Analysis
- SWOT: Offers a more detailed examination of internal attributes and factors.
- PESTEL: Provides a comprehensive assessment of the external environment's six major categories.
When to Use SWOT vs. PESTEL Analysis
Use SWOT Analysis When:
- You want to assess your organization's current state, internal capabilities, and competitive positioning.
- You need to make short-term decisions and address immediate challenges.
- You are focused on understanding how internal strengths and weaknesses align with external opportunities and threats.
Use PESTEL Analysis When:
- You are engaging in long-term strategic planning and need to anticipate future trends and potential disruptions.
- You want to gain a comprehensive understanding of the external macro-environment and its impact on your business.
- You need to identify emerging opportunities and threats beyond your organization's immediate control.
In many cases, organizations use both SWOT and PESTEL analyses in conjunction to create a well-rounded strategic plan. SWOT helps organizations identify internal factors that can be leveraged or improved, while PESTEL highlights the external forces shaping the business landscape. Together, these analyses provide a holistic view that guides informed decision-making and strategic direction.
What is the PESTEL Framework?
Let's explore the PESTEL framework in more detail, breaking down each of its six key components.
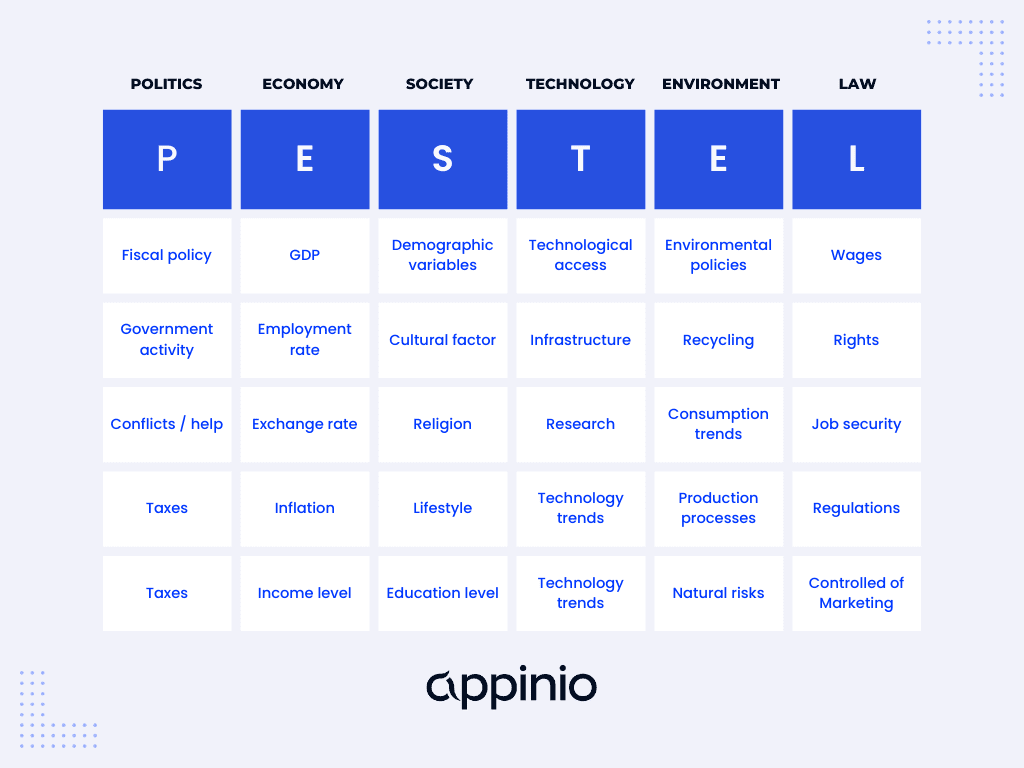
Political Factors
Political factors encompass the influence of government policies, regulations, and the political environment on a business. These factors can have a profound impact on how a company operates, its profitability, and its strategic decisions.
Political factors to consider include:
- Government Stability: The stability of a government can affect the long-term planning and investment decisions of businesses. In regions with frequent political upheaval, businesses may face higher risks.
- Taxation Policies: Different tax rates and policies can directly impact a company's profitability and cost structure. Understanding tax laws is crucial for financial planning.
- Trade Regulations: International trade agreements and tariffs can affect the ease of conducting business across borders. Changes in trade policies can disrupt supply chains and market access.
- Political Ideologies: The political climate, including ideologies and values held by governments, can shape consumer sentiment and influence market dynamics.
Economic Factors
Economic factors delve into the economic conditions within which a business operates. These conditions can substantially affect a company's performance and strategy.
Key economic factors include:
- Inflation Rates: High inflation can erode purchasing power, affecting consumer spending and the cost of doing business.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact international trade, affecting both imports and exports.
- Economic Growth: A country or region's overall economic growth rate can influence market expansion opportunities and consumer demand.
- Consumer Confidence: The confidence consumers have in the economy can impact their spending habits. High consumer confidence often leads to increased consumption.
Social Factors
Social factors focus on the societal aspects that can shape a business's success. Understanding the social context is essential for effective marketing and product development.
Key social factors include:
- Demographics: The age, gender, income, and cultural background of the population can affect product preferences and market segmentation.
- Cultural Norms: Understanding cultural values, customs, and beliefs is vital for marketing and product adaptation.
- Lifestyle Trends: Changes in lifestyle trends, such as health consciousness or digitalization, can create new opportunities or threats.
- Consumer Behavior: Analyzing consumer behavior, including buying patterns and preferences, helps tailor marketing strategies.
Technological Factors
Technological factors involve the impact of technological advancements on a business or industry. Staying technologically current is critical for competitiveness.
Key technological factors include:
- Innovation: The rate of technological innovation can determine the lifespan of products and services and influence a company's competitiveness.
- Automation: Adopting automation and artificial intelligence can affect labor costs and operational efficiency.
- Research and Development: The level of investment in research and development influences a company's ability to introduce new products and services.
- Technological Disruption: Industries are susceptible to technological disruption; staying aware of potential disruptions is crucial for strategic planning.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors consider the influence of ecological and environmental conditions on a business. Increasingly, businesses are expected to operate sustainably.
Important environmental factors include:
- Sustainability Practices: Consumers are increasingly eco-conscious, and businesses adopting sustainable practices can gain a competitive advantage.
- Climate Change: Climate-related factors, such as extreme weather events, can impact supply chains and operations.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations may require businesses to invest in eco-friendly technologies and processes.
- Resource Availability: The availability of key resources, such as water or rare minerals, can affect production and sourcing.
Legal Factors
Legal factors encompass the legal framework within which a business operates. Compliance with laws and regulations is critical for avoiding legal issues.
Relevant legal factors include:
- Employment Laws: Regulations governing employment relationships, wages, and benefits can affect labor costs and HR policies.
- Intellectual Property: Protection of intellectual property rights is essential to safeguard innovations and competitive advantages.
- Industry-specific Regulations: Different industries are subject to specific regulations; understanding and compliance are crucial.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws affect marketing, product safety, and customer relations.
By understanding the nuances of each PESTEL factor, you can conduct a more comprehensive analysis of your business environment and make well-informed strategic decisions.
How to Conduct a PESTEL Analysis?
Now that you have a clear understanding of the PESTEL framework, let's explore the step-by-step process of conducting a PESTEL analysis for your business.
Step 1: Identify Relevant Factors
The first step in conducting a PESTEL analysis is to identify the factors within each category that are most relevant to your business or industry. While all six categories are important, not every factor may have equal significance for your specific situation.
- Brainstorm and List Factors: Start by brainstorming and listing all potential factors within each category. This can be done through internal discussions, industry research, and stakeholder input.
- Filter and Prioritize: Evaluate the listed factors to determine their relevance and potential impact. Consider the current state of your business and industry trends. Prioritize the most influential factors.
- Focus on Key Influencers: Concentrate on the key factors likely to affect your business strategy, decision-making, and long-term planning. These factors will be the focus of your analysis.
Step 2: Gather Information and Data
Once you've identified the key factors to analyze, the next step is to gather relevant information and data. Accurate and up-to-date information is crucial for conducting a meaningful PESTEL analysis.
- Utilize Multiple Sources: Gather data from various sources, including government reports, industry publications, market research, and reliable news outlets. Diverse sources provide a more comprehensive perspective.
- Market Research: Conduct market research to understand consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes. Surveys and interviews with stakeholders can provide valuable insights.
- Data Collection Methods: Employ quantitative and qualitative data collection methods as appropriate. Statistical data, surveys, and expert opinions can all contribute to your analysis.
- Historical Data: Analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns. Understanding past developments can help predict future outcomes.
Step 3: Analyze Each Factor
With the relevant data in hand, it's time to analyze each factor systematically. This step involves a thorough assessment of how each factor may impact your business.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluate the potential impact of each factor on your business. Consider both the magnitude of the impact and the likelihood of occurrence.
- Scoring System: Some businesses use a scoring system to quantify the impact of each factor. Assign numerical values to factors based on their significance, with higher scores indicating greater importance.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and opportunities associated with each factor. Are they primarily threats, opportunities, or both? Understanding this helps in risk mitigation and strategy development.
- Interconnectivity: Recognize that these factors are not isolated. They often interact with one another. Analyze how changes in one factor may trigger changes in others.
Step 4: Interpret the Impact on Business
The final step of a PESTEL analysis involves interpreting the collective impact of the analyzed factors on your business.
- Synthesize Findings: Summarize your findings from the analysis of each factor. Highlight key insights and trends that emerged during the assessment.
- Strategic Implications: Consider how these insights should inform your business strategy. What changes or adaptations are necessary in response to the identified opportunities and threats?
- Scenario Planning: Develop scenarios for different external conditions based on your analysis. This allows your business to prepare for a range of potential futures.
- Continuous Monitoring: Recognize that the external environment is dynamic. Regularly review and update your PESTEL analysis to stay responsive to changing conditions.
By following these steps, you can conduct a comprehensive PESTEL analysis that equips your business with valuable insights and a strategic roadmap for navigating the external factors that impact your operations.
Practical Applications of PESTEL Analysis
Now that you understand how to conduct a PESTEL analysis, let's explore its real-world use cases and applications in various aspects of business strategy and decision-making.
Business Strategy Development
PESTEL analysis serves as a powerful tool for shaping your business strategy. Here's how it contributes to the development of effective strategies:
- Alignment with External Environment: PESTEL analysis ensures that your business strategy aligns with the external factors that can influence your operations. By considering political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors, you can develop adaptable and responsive strategies to changes in the business environment.
- Identifying Opportunities: It helps identify opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, recognizing a shift in consumer behavior towards sustainability can prompt the development of eco-friendly products, giving your business a competitive edge.
- Threat Mitigation: On the flip side, PESTEL analysis helps you proactively identify threats and challenges. Whether it's anticipating regulatory changes or economic downturns, having a clear understanding of potential obstacles allows you to implement mitigation strategies.
- Long-term Planning: Effective business strategies require a long-term perspective. PESTEL analysis provides insights into long-term trends and factors, enabling you to make decisions that will benefit your business in the years to come.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk is an inherent part of business, but PESTEL analysis can help you assess and mitigate potential risks effectively:
- Identifying Risk Factors: By systematically evaluating political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors, you can pinpoint the factors most likely to pose risks to your business.
- Quantifying Risk: Some organizations assign numerical values to risk factors to quantify their potential impact and likelihood. This allows for a more structured approach to risk assessment.
- Developing Contingency Plans: Armed with insights from PESTEL analysis, you can develop contingency plans to address potential risks. These plans outline specific actions to take if certain risk scenarios materialize.
- Resource Allocation: Knowing where potential risks lie helps you allocate resources more efficiently. You can direct resources toward areas that require greater attention and risk mitigation.
Market Research and Entry
Expanding into new markets or even understanding your current market better requires a deep understanding of the external environment. PESTEL analysis aids in market research and entry strategies:
- Market Selection: PESTEL analysis assists in the selection of markets with the most favorable external conditions for your products or services. Factors like political stability, economic growth, and cultural alignment are considered.
- Adaptation to Local Context: In international markets, cultural and social factors significantly influence consumer preferences. PESTEL analysis helps tailor marketing and product strategies to fit the local context.
- Compliance and Regulation: Different markets have varying legal and regulatory frameworks. PESTEL analysis ensures you are aware of compliance requirements and potential legal challenges.
- Competitive Intelligence: PESTEL analysis can also reveal insights into the competitive landscape of a new market. Understanding how external factors affect your competitors can inform your market entry strategy.
Competitive Analysis
Comparing your PESTEL analysis with that of your competitors can provide a competitive edge:
- Identifying Differential Factors: By comparing your strengths and weaknesses against those of competitors in each PESTEL category, you can identify areas where you have a competitive advantage or where you need improvement.
- Benchmarking: PESTEL analysis enables benchmarking against industry standards. This helps in setting realistic goals and targets for your business.
- Strategic Positioning: Understanding how external factors impact your competitors' strategies can help you strategically position your business to exploit market gaps or challenges they may face.
Scenario Planning
Scenario planning involves creating hypothetical situations based on different external conditions and using them to make strategic decisions:
- Utilizing PESTEL Factors: PESTEL analysis provides the foundational data for scenario planning. You can use insights from your analysis to create scenarios based on changes in political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors.
- Risk Mitigation: Scenario planning allows you to develop pre-defined responses to various scenarios, helping you mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities as they arise.
- Flexibility in Decision-Making: With a library of scenarios at your disposal, you can make more agile and informed decisions when faced with unexpected changes in the external environment.
- Long-term Strategy: Scenario planning extends your strategic planning horizon, enabling your business to navigate uncertainty and remain competitive in the long run.
Incorporating PESTEL analysis into these practical applications empowers your business to make informed decisions, adapt to changing conditions, and gain a competitive advantage in a dynamic business environment.
PESTEL Analysis Examples
To better understand how PESTEL analysis is applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some concrete examples across different industries. These examples illustrate how organizations use PESTEL analysis to make informed decisions, adapt to changing circumstances, and seize opportunities.
Tech Giant's Market Entry Strategy
Industry: Technology
A global technology company planning to enter a new international market uses PESTEL analysis as a vital part of its strategy. Here's how it applies each factor:
- Political: Assess the political stability and regulatory environment of the target country. Analyze factors like data privacy laws, intellectual property protection, and government support for tech innovation.
- Economic: Examine the economic conditions, including GDP growth, currency exchange rates, and taxation. Evaluate the potential market size and consumers' purchasing power.
- Social: Study local consumer behavior, preferences, and cultural trends. Understand how social factors may impact product adoption and marketing strategies.
- Technological: Analyze the state of technology infrastructure and digital readiness in the target market. Consider how technological advancements may influence product development and innovation.
- Environmental: Evaluate environmental regulations and sustainability concerns. Determine whether the company's products align with local environmental standards and consumer expectations.
- Legal: Identify legal requirements for market entry, including trade agreements, import/export regulations, and industry-specific laws.
Pharmaceutical Company's Regulatory Compliance
Industry: Healthcare/Pharmaceuticals
A pharmaceutical company operating in multiple countries conducts PESTEL analysis to ensure regulatory compliance and adapt to changing healthcare landscapes:
- Political: Stay informed about changes in healthcare policies and regulations in each market. Comply with drug approval processes, pricing controls, and healthcare funding policies.
- Economic: Monitor economic conditions affecting healthcare spending. Adjust pricing strategies and market access plans based on economic factors such as healthcare budgets and insurance coverage.
- Social: Consider social factors like public health trends, patient preferences, and demographics. Tailor marketing strategies to address specific healthcare needs and patient expectations.
- Technological: Embrace technological advancements in pharmaceutical research, manufacturing, and digital health solutions. Leverage technology to enhance drug development and patient engagement.
- Environmental: Comply with environmental regulations related to pharmaceutical manufacturing, waste disposal, and sustainable practices. Invest in eco-friendly initiatives and sustainable packaging.
- Legal: Stay up-to-date with changing healthcare laws and intellectual property regulations. Ensure compliance with patent laws and generic drug competition.
Automaker's Electric Vehicle (EV) Strategy
Industry: Automotive
An automotive company plans to transition into electric vehicles (EVs) to meet growing consumer demand and sustainability goals:
- Political: Evaluate government incentives and regulations promoting EV adoption. Assess potential subsidies, tax credits, and emission standards favoring electric vehicles.
- Economic: Analyze economic factors impacting the EV market, such as consumer willingness to pay for electric cars and the availability of charging infrastructure.
- Social: Understand the social shift toward environmental consciousness and green transportation. Tailor marketing campaigns to appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
- Technological: Invest in EV technology advancements, including battery efficiency and autonomous driving features. Stay competitive by embracing cutting-edge technology.
- Environmental: Demonstrate commitment to sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint in manufacturing and promoting the eco-friendliness of EVs.
- Legal: Comply with safety regulations specific to electric vehicles and address legal challenges related to autonomous driving technology.
Hotel Chain's Expansion into Emerging Markets
Industry: Hospitality
A hotel chain plans to expand into emerging markets to tap into growing tourism. PESTEL analysis helps assess the feasibility and risks:
- Political: Evaluate the political stability and government policies related to tourism and foreign investment. Ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Economic: Analyze economic conditions impacting travel, including currency exchange rates, inflation, and disposable income levels. Adjust pricing strategies accordingly.
- Social: Understand cultural norms, traveler preferences, and social trends in the target markets. Customize services and amenities to meet local expectations.
- Technological: Embrace technology for online booking, guest management, and marketing. Ensure seamless integration with mobile apps and digital platforms.
- Environmental: Address sustainability concerns by implementing eco-friendly practices, such as energy-efficient lighting and waste reduction.
- Legal: Comply with local labor laws, licensing requirements, and health and safety regulations in each country of operation.
To unlock exclusive insights into the ever-evolving travel landscape, download the Travel & Tourism Appinio Hype Tracker Report featuring expert analysis from Jonas Upmann of HomeToGo. Dive into the latest trends and challenges shaping the industry, and gain a comprehensive understanding of how American travelers are adapting to this dynamic environment.
Download the report now for a deeper insight into the future of travel!
These examples demonstrate how organizations from various industries leverage PESTEL analysis to navigate complex external environments, make informed decisions, and tailor their strategies to unique circumstances. By considering political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors, businesses can stay agile and responsive in an ever-changing world.
Best Practices for Conducting a PESTEL Analysis
While understanding the components and steps of PESTEL analysis is crucial, it's equally important to follow best practices to ensure the effectiveness of your analysis.
- Collaborative Approach: Involve a cross-functional team in the analysis process. Different departments within your organization may have unique insights into the impact of external factors on the business. Collaborative input ensures a comprehensive assessment.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Thoroughly research and gather data from a wide range of sources. Don't rely solely on one data point or information from a single source. Utilize government reports, industry publications, market research, and stakeholder interviews to obtain a holistic view of the external environment.
- Continuous Monitoring: Recognize that the external environment is dynamic and subject to change. Regularly update your PESTEL analysis to stay current with evolving factors. Implement a systematic review schedule to ensure your analysis remains relevant.
- Prioritization: Not all factors are equally important or impactful. Prioritize the most influential factors based on their potential to affect your business. Develop a scoring system or ranking mechanism to allocate resources and attention effectively.
- Scenario Planning: Extend your analysis to scenario planning. Create hypothetical scenarios based on various combinations of external conditions. These scenarios help you anticipate and prepare for potential futures, making your strategic decision-making more robust.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Compare your PESTEL analysis with that of your competitors. Understanding how external factors are affecting your competitors' strategies can provide insights and competitive advantages. Identify gaps or opportunities where your organization can excel.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identify potential risks and challenges associated with each factor. Develop contingency plans to address these risks proactively. By having pre-defined responses in place, you can minimize the impact of unexpected changes in the external environment.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage with stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and industry experts, to gather insights and validate your analysis. Their perspectives can provide valuable real-world context to your findings.
- Regular Review and Reporting: Establish a reporting mechanism to communicate your PESTEL analysis findings to key decision-makers within your organization. Regularly review and update the analysis to ensure alignment with strategic goals and objectives.
- Integration with Other Strategic Tools: Integrate PESTEL analysis with other strategic planning tools such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), Porter's Five Forces analysis, and the Balanced Scorecard. Combining these tools provides a comprehensive framework for strategic decision-making.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure that your team members are knowledgeable about PESTEL analysis and its significance. Offer training and awareness programs to foster a culture of strategic thinking and adaptability within your organization.
By adhering to these best practices, you can maximize the effectiveness of your PESTEL analysis, make informed decisions, and navigate the dynamic external business environment more successfully. PESTEL analysis, when executed well, becomes a strategic asset that guides your organization toward sustainable growth and resilience.
Conclusion for PESTEL
PESTEL analysis empowers you to see the bigger picture and make well-informed decisions. By understanding the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors surrounding your business, you can adapt, grow, and thrive in a constantly changing world.
So, whether you're a tech giant eyeing global expansion, a healthcare leader navigating regulatory challenges, or any organization seeking to stay ahead, PESTEL analysis is your compass in the complex journey of strategic planning.
How to Conduct PESTEL Analysis in Minutes?
Appinio, the real-time market research platform, revolutionizes your PESTEL analysis by providing swift access to crucial consumer insights.
- Lightning-Fast Results: Get from questions to insights in minutes, ensuring you make timely and informed decisions.
- User-Friendly Interface: No research PhD required! Appinio's intuitive platform empowers anyone to conduct comprehensive PESTEL analyses effortlessly.
- Global Reach: With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define precise target groups using 1200+ characteristics, you'll have a truly global perspective.
Want to try it out yourself? Then download our PESTEL analysis template directly to use!

Or dive in deeper and try out a combination of our methods to get the best market overview for your business project or strategy within our platform!
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!